Blog
What is Interoperability in Healthcare?
Interoperability Definition
HIMSS (Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society) defines interoperability as:
The extent to which systems and devices can exchange data, and interpret that shared data. For two systems to be interoperable, they must be able to exchange data and subsequently present that data such that it can be understood by a user.
In simple terms it means various healthcare systems can communicate seamlessly with each other making medical data universally available.
Interoperability in Healthcare Data: A Life-Saving Advantage
When health system clinicians make care decisions based on their organization’s EHR data alone, they’re only using a small portion of patient health information. Additional data sources such as health information exchanges (HIEs) and patient-generated and reported data round out the full picture of an individual’s health and healthcare needs. This comprehensive insight enables critical, and sometimes life-saving, treatment and health management choices. To leverage the data from beyond the four walls of a health system and combine it with clinical, financial, and operational EHR data, organizations need an interoperable platform approach to health data. The Health Catalyst® Data Operating System (DOS™), for example, combines, manages, and leverages disparate forms of health data for a complete view of the patient and more accurate insights into the best care decisions.
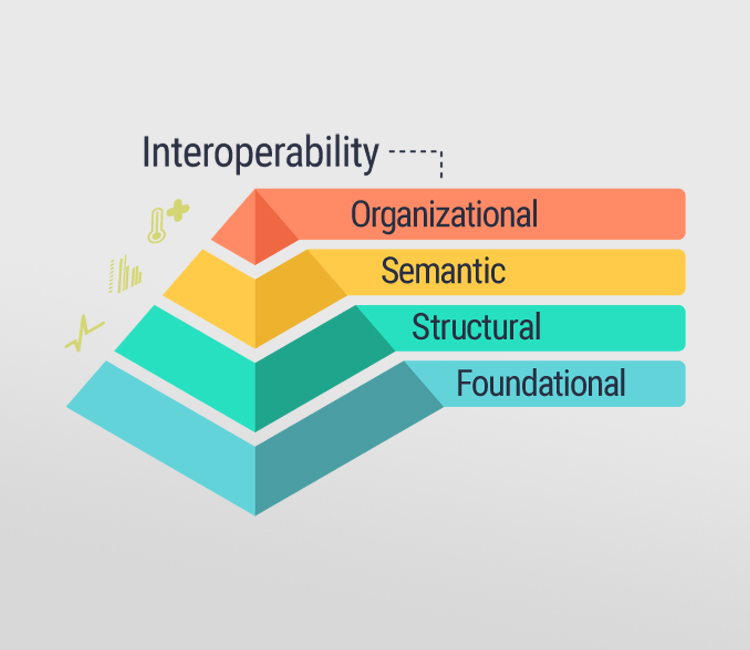
Four Levels of Interoperability
- Foundational (Level 1): Establishes the inter-connectivity requirements needed for one system or application to securely communicate data to and receive data from another.
- Structural (Level 2): Defines the format, syntax and organization of data exchange including at the data field level for interpretation.
- Semantic (Level 3): Provides for common underlying models and codification of the data including the use of data elements with standardized definitions from publicly available value sets and coding vocabularies, providing shared understanding and meaning to the user.
- Organizational (Level 4): Includes governance, policy, social, legal and organizational considerations to facilitate the secure, seamless and timely communication and use of data both within and between organizations, entities and individuals. These components enable shared consent, trust and integrated end-user processes and workflows.
What is Health Information Exchange and Data Sharing?
Health information exchange, or HIE, provides the capability to electronically move clinical information among disparate healthcare information systems and maintain the meaning of the information being exchanged. The goal of health information exchange is to facilitate access to and retrieval of clinical data to provide safe, timely, efficient, effective and equitable patient-centered care. HIE can also be used by public health authorities to assist in the analysis of the health of populations.
The benefits of interoperability in health care
Providers and plans are likely to see the highest ROI through the following:
- Reduction in administrative costs
- Increased efficiency of care delivery
- Reduction in the total cost of care
- Increased revenue and growth
Reduction in administrative costs
Interoperability in health care can enable both provider and plan organizations to reduce or redeploy FTEs away from time-consuming manual processes that often do not create value to tasks that can directly reduce health care costs and improve quality.
Increased efficiency of care delivery
Radical interoperability in health care allows clinicians access to real- or near-real-time data wherever care is being delivered. These capabilities can also enable clinicians to change how care is delivered, both in terms of where care is delivered and who delivers it, in order to increase the number of patients receiving care.
Reduction in the total cost of care
While health plans have always strived to reduce the amount of health care services utilized, providers in value-based care (VBC) reimbursement models are now incentivized to take similar steps.
Increased revenue and growth
The organizations leveraging technology to make interoperability in health care happen faster will likely acquire and retain patients most effectively. Plans and providers are shifting their focus to the health care consumer, who can drive revenue and growth.
References:
Recent Posts
Archives
- December 2024
- November 2024
- October 2024
- September 2024
- August 2024
- April 2024
- February 2024
- January 2024
- April 2022
- November 2021
- August 2021
- May 2021
- April 2021
- March 2021
- February 2021
- December 2020
- November 2020
- October 2020
- July 2020
- April 2020
- December 2019
- October 2019
- August 2019
- July 2019
- June 2019
- April 2019

