PACS system radiology
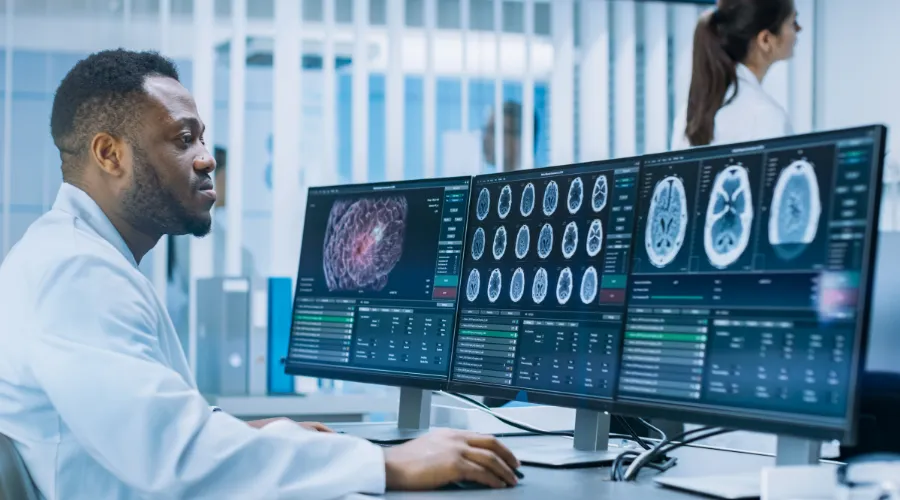
PACS system radiology is a secure, reliable method to store, retrieve, and transport medical images. It provides benefits, such as remote access, and better-organized patient data.
They eliminate the need for hard-copy films and use digital images instead. This can help with providing better patient care and making more accurate diagnoses, especially in radiology.
What is PACS?
PACS stands for Picture Archiving and Communication System. It securely transports medical imaging information, allowing healthcare professionals to store and transmit images and clinical reports.
How does it work?
The PACS system stores and transfers medical images in DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) format and supports several functions:
- Image acquisition: Medical images are digitally captured from multiple imaging methods, such as X-ray, CT, and MRI, adhering to DICOM standards.
- Image transfer and storage: These digital images are sent to the PACS server that stores and archives them in a central database.
- Image distribution and viewing: Radiologists can access and view stored images from any PACS workstation connected to the network.
- Reporting: Radiologists can create and save diagnostic reports with their images in the PACS.
- Integration: PACS systems can integrate with other systems, such as RIS (Radiology Information System).
PACS and RIS
PACS can integrate with the Radiology Information System (RIS), enabling bi-directional communication between the systems. RIS sends patient data to PACS, and PACS returns acquired images and reports, allowing a coordinated radiology workflow.
Importance of PACS in radiology
Radiologists benefit from PACS in many ways, including:
- Remote access: PACS enables radiologists to access diagnostic images anytime, improving diagnosis accuracy, speed, and healthcare quality.
- Film archives replacement: PACS eliminates the need for film archives, reduces physical storage requirements, and promotes efficient cooperation across departments.
- Easy for radiologists: Radiologists can use the PACS system to manage their work. They take the necessary images, review them in the workstation, sending them to the digital archive, and the images are now available for healthcare professionals who have access to the PACS system.
Types of PACS systems
Types of PACS systems include:
1. Traditional PACS
Traditional PACS represents the cornerstone of image storage, retrieval, and distribution within a local network.
They offer strong control and privacy but it’s limited by physical space and requires continuous maintenance.
Traditional PACS are perfect for facilities that prefer keeping all operations in-house and have the necessary infrastructure.
2. Cloud-based PACS
They are more modern than traditional PACS, as they benefit from the internet for image storage and management. The images can be accessed from any device, at any time without great concern about physical storage limitations or maintenance.
They offer scalable storage solutions, usually requiring a subscription.
3. Hybrid systems
Hybrid systems blend traditional and cloud-based PACS. They offer the best of both systems:
- Control and Security
- flexibility and scalability of the cloud
They are fit for those looking forward to maintaining on-site backup while taking advantage of cloud storage as well.
Benefits of PACS system radiology
Medical PACS systems can provide a lot of benefits, especially in the radiology field. Some of these benefits include:
- More efficient diagnoses
- Reduced costs
- High-quality medical images
- Instant remote access for medical images
- Increased integration between departments and facilities
- Improve patient care
- Ease of use and scalability of cloud-based PACS
For more details about some of the benefits:
- Reduced costs: Digital storage is generally less expensive than storage needed for hard-copy films, which makes the PACS system a cost-effective solution.
- Better patient data management: All patient information can be accessed through a single point of access as images are integrated with the radiology information system.
- Faster workflow: There’s no need for manual transport and retrieval of images. It’s a rapid process with the help of the PACS system, as radiologists can access images quickly and provide better patient care.
Best PACS system radiology
The best PACS system according to the number of installs includes:
- GE Healthcare – Centricity
- Change Healthcare – Radiology Solutions
- FUJIFILM Medical Systems – Synapse
- IBM – Merge PACS
- Philips Healthcare – iSite
- Agfa Healthcare – Impax
- Novarad – NovaPACS
- Sectra – SectraPACS
- Carestream Health – Carestream vue
- Change Healthcare
PACS system radiology cost factors
How much does a PACS system cost? There are many factors affecting the cost of the PACS system, such as:
- Total storage capacity: Solid-state storage (SSD) is more available and much faster to access than spinning disks (HDD). SSD costs about double the similar capacity of disk storage.
- Maintenance and support: The PACS system requires annual maintenance and support which may affect the cost of the PACS system.
- Type of PACS system used: Also choosing the appropriate type of PACS system for you may influence the total cost.
FAQs
What is the PACS system in radiology?
PACS system is a secure method to store and transport medical images according to DICOM format. It helps radiologists to access diagnostic images anywhere, sharing images with other healthcare professionals, and providing better patient care.
What are the main components of PACS?
PACS system for radiology components include:
- Main server: The main server is the most important part of a PACS. It includes the database structure, RIS interface, web servers, and other image distribution servers and interfaces.
- Database: This refers to the place at which all the important information is stored including all the data related to the patient study and examination.
- Health level seven (HL7): The HL7 is the part that receives all the info caused by RIS and then forwards it to the PACS.
- Imaging modalities: These are machines used to capture digital medical images, such as X-ray machines, MRI machines, and Ultrasound equipment.
- Workstations: These are computers equipped with DICOM viewers that allow radiologists to access, view, and interpret stored images.
- Storing archives: DICOM images are stored in the servers or cloud storage, either on-site, in the cloud, or both (hybrid).
A secure network connection is also necessary for the healthcare PACS system to work efficiently.
Recent Posts
Archives
- December 2024
- November 2024
- October 2024
- September 2024
- August 2024
- April 2024
- February 2024
- January 2024
- April 2022
- November 2021
- August 2021
- May 2021
- April 2021
- March 2021
- February 2021
- December 2020
- November 2020
- October 2020
- July 2020
- April 2020
- December 2019
- October 2019
- August 2019
- July 2019
- June 2019
- April 2019