Radiology teaching files are powerful tools for radiologists. They allow the archiving of interesting cases to ensure important findings are not missed while also enhancing diagnostic skills.
These teaching files serve multiple purposes, whether it’s for educating radiology students, discussing cases with colleagues, contributing to the medical community, or keeping up with effective e-learning methods for radiology.
What Are Teaching Files?
Radiology teaching files are collections of clinical cases with teaching value.
These files provide real examples of radiology cases that may help with teaching purposes, whether for radiologists or radiology students.
Generally, radiology education relies on studying and referencing previous patient cases but storage, accessibility, and shareability with students can present challenges. Additionally, studies should be anonymized.
So, radiology teaching files can serve several purposes, such as:
- To ensure important findings are not missed.
- Archiving cases for clinical follow-up.
- As a reference for better understanding diseases.
- Facilitating secure Knowledge transfer and assessment.
- Enabling quick retrieval of anonymized patient cases.
Structure Of Radiology Teaching Files
Radiology teaching files are organized to make them easy for learners to navigate and understand. Each case typically includes:
- Patient information: This Includes the patient’s age, gender, medical history, and symptoms.
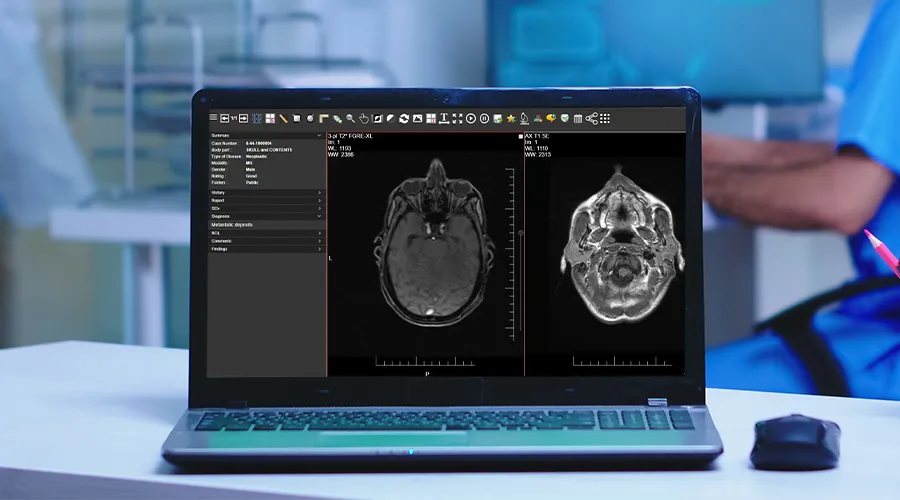
- Imaging studies: X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, or ultrasounds are often presented in multiple views to better understand the cases.
- Annotations and labels: Key areas of the image are often highlighted to direct the learners to a significant finding.
- Diagnosis and discussion: A detailed explanation of the diagnosis, including why certain findings on the images led to that conclusion.
- Teaching points: Summary points that highlight important lessons from the case.
Teaching Files Types
Teaching files can be divided into three types:
1. Personal Teaching Files
Personal teaching files are for individual use. The owner may have an interest in a very specific case for quality control, reviewing his work, teaching, or clinical follow-up.
2. Shared In-House Teaching Files
Personal teaching files can be migrated into a shared teaching file environment. Additional information can be added to make the case available for colleagues to view and learn from.
3. Public Teaching Files
They are built on a shared teaching files model but contain more comprehensive content. They may undergo a formal review before publication and sometimes require a subscription fee.
Teaching File Case Types
Teaching file case types include:
1. Cardiac
Cardiac teaching files focus on heart-related cases and cardiovascular conditions. They include imaging for:
- coronary artery disease
- congenital heart anomalies
- heart failure
- valvular diseases
- others
Radiologists can use these files for better understanding of heart structure and function. Files can be also helpful for assessment of cardiac conditions.
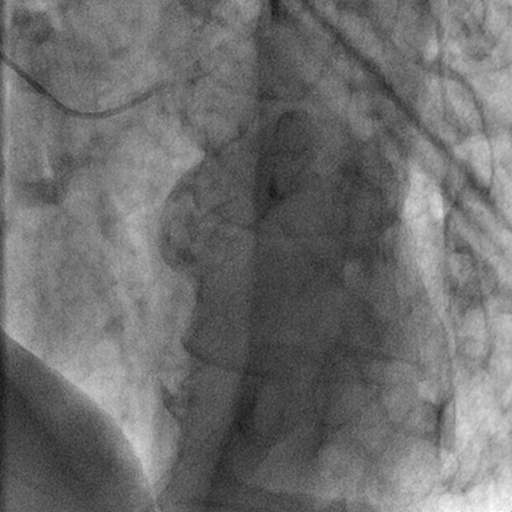
2. Chest
Chest teaching files cover diseases of the chest, such as:
- pneumonia.
- chest tumors.
- interstitial lung diseases.
- pleural abnormalities.
They help radiologists enhance their skills in chest cases.
3. Gastrointestinal
Gastrointestinal teaching files focus on the digestive system including the esophagus, stomach, intestines, liver, pancreas, and biliary system.
They include cases of various gastrointestinal diseases, such as:
- Liver diseases
- Colorectal cancers
- pancreatitis
- bowel obstruction
Radiologists can archive these teaching files for educational purposes or to enhance their skills.
4. Genitourinary
These files focus on the urinary and reproductive systems. Files can include:
- Renal cell carcinoma
- Polycystic kidney disease
- Urinary tract infections
- Urinary stones
- Hydronephrosis
- Ovarian masses
These files help radiologists assess urological structure and functions and improve their experience in the diagnosis of urinary tract masses and pathologies.

5. Interventional
Interventional teaching files include some procedures, such as:
- Biopsies
- Catheter placements
- Angioplasty
- Tumor ablation
These cases help radiologists learn more about the procedures and improve patient management skills.
6. Mammography
Mammography files specialize in breast imaging cases, such as:
- Breast tumors
- Fibrocystic changes
- Breast cysts
- Ductal carcinoma in situ
Radiologists can gain valuable experience in breast cases through mammography teaching files.
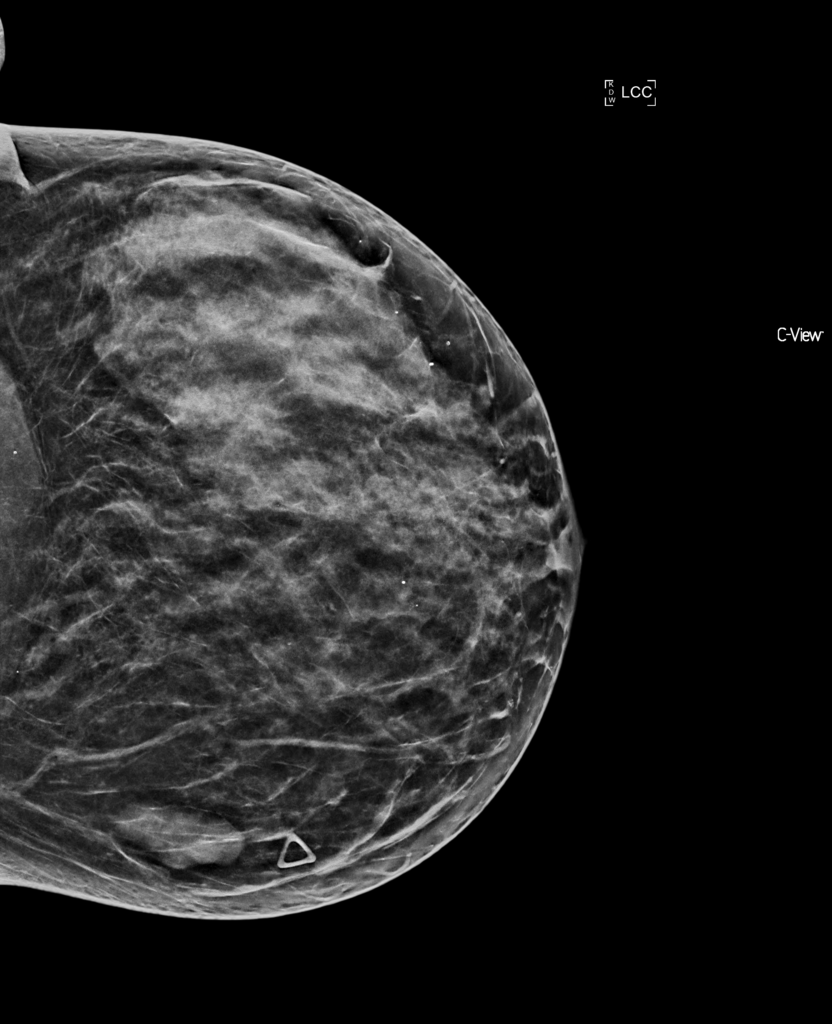
7. Musculoskeletal
Musculoskeletal teaching files focus on improving radiologist’s skills in recognizing bone and soft tissue abnormalities, such as:
- Osteoarthritis
- Soft tissue tumors
- Fractures
- Bone tumors
- Sports-related injuries
8. Neuroradiology
Neuroradiology files guide radiologists in recognizing brain abnormalities and how to differentiate normal from abnormal brain or nervous structure. They cover cases, such as:
- Stroke
- Brain tumors
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Traumatic brain injuries
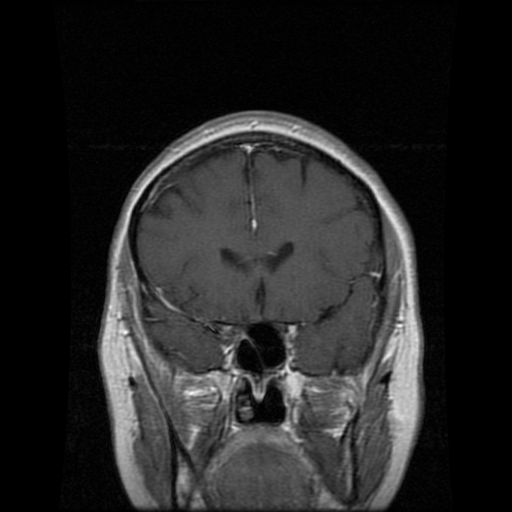
9. Nuclear Medicine
These files cover radiotracer use, interpretation of uptake patterns, and correlation with clinical scenarios. They provide cases like:
- Thyroid nodules
- Bone metastases
- Neuroendocrine tumors
10. Pediatrics
Pediatric files train radiologists to recognize specific conditions in children. Pediatric cases often include:
- Rickets
- Congenital malformations
- Neuroblastoma
- Pediatric trauma
- Respiratory conditions
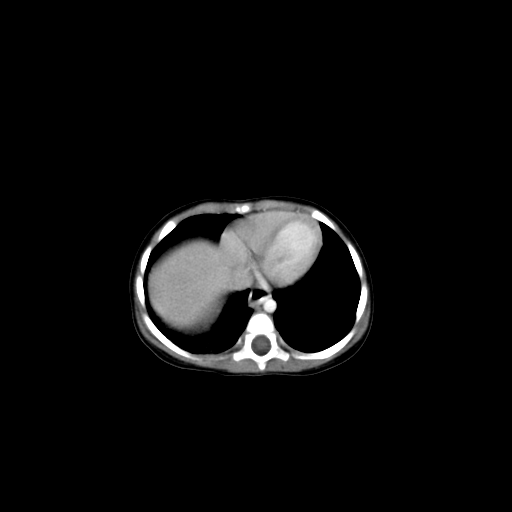
11. Ultrasound
Ultrasound case studies are essential for helping radiologists identify numerous conditions and enhance their diagnostic skills. They may include cases on:
- Gallstones
- Liver disease
- Obstetric and gynecologic conditions
- Thyroid nodules
- Abdominal conditions
- Vascular conditions
Importance Of Teaching Files For Radiologists
Radiologists may be advised to build their teaching files for the following reasons:
1. Increase Your Expertise
Establishing teaching files encourages radiologists to engage with cases on a deeper level.
It fosters critical thinking in analyzing images, making accurate diagnoses, and explaining findings.
This process sharpens diagnostic skills and enhances a radiologist’s level of experience.
2. Education Purposes
Radiology teaching files enrich the medical community by providing real and often interesting cases. This helps medical students, radiologists, and colleagues. Importantly, difficult cases recorded in teaching files will be more easily diagnosed in the future.
3. Self-Learning And Review
Teaching files are not only for the broader medical community but can also serve as a valuable personal learning resource. Having cases documented allows radiologists to review challenging cases, rare pathologies, or those with subtle findings.
iCode Teaching Files
iCode Teaching Files is a web teaching files solution that helps radiologists archive their interesting studies and build imaging libraries according to ACR standards.
It archives interesting cases on a separate server with a separate database. You can keep the radiology teaching archive safe when the PACS vendor is changed.
Examples of iCode teaching files features include:
- Easy file search and retrieval
- Robust data anonymisation
- Ability to export studies with several media files, such as presentations, videos, JPEG, TIFF & DICOM..etc
- Manage teaching events easily with a streamlined workflow and lectures bank to enhance learning
- Building scalable teaching archive across specific region or country.
iCode Teaching Files Radiology Exam System
The iCode Teaching File Solution is revolutionizing radiology education with its comprehensive exam module, designed to enhance both teaching and learning.
This system assists radiologists in creating radiology exams for their students. The exam module in iCode Teaching Files allows radiologists to craft multiple-choice questions (MCQs) based on archived medical images.
It also enables educators to share quiz links with their students, allowing them to take exams directly through the teaching files system.
With detailed analytics and instant feedback, both learners and educators can track progress and identify areas for improvement, ultimately elevating the quality of training.
iCode offers a rich set of features tailored to meet your educational needs, enabling you to archive cases quickly and effortlessly. Additionally, its comprehensive exam module supports and enhances the educational process.