Blog

Integration of Health Information Systems to Promote Health
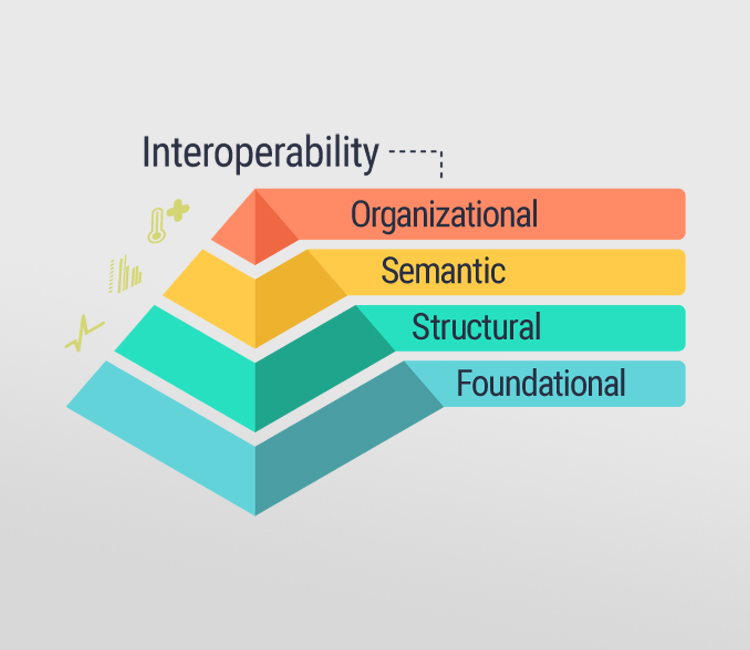
Healthcare IT integration is a combination of IT and healthcare sector and involves the application of latest IT solutions to monitor people’s health, perform secured exchange of their electronic data and provide economical healthcare solution. The purpose of integrating health systems is to provide seamless services; make them more accessible, easy to understand and use; and lead to better overall patient health.
The major factors that will accelerate the growth of the healthcare IT integration market are high healthcare costs, government initiatives to curb this rising cost and the growing demand to incorporate IT in the healthcare domain. Healthcare IT Integration Market is valued at 3.15 USD Billion in 2019 and expected to reach 6.21 USD Billion by 2026 with the CAGR of 10.2% over the forecast period.
The healthcare IT integration market has been categorized on the basis of product and services, and application. The products in healthcare IT integration market include interface/integration engines, media integration solutions, medical device integration software, and other integration tools. Based on the services provided, the market is segmented into implementation services, support and maintenance services, and training services.
Based on application, the market is segmented into hospital integration, clinic integration, lab integration, radiology integration, medical device integration and others. Due to the multiple applications of IT integration in hospitals, that encourage value based healthcare reimbursement, the hospital integration segment holds the largest share and is expected to witness growth during the forecast period.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
By Product, Services & Application
- By Product
- Interface/Integration Engines
- Media Integration Solutions
- Medical Device Integration Software
- Other Integration Tools
- By Services
- Implementation services
- Support and maintenance services
- Training services
- By Application
- Hospital integration
- Clinic integration
- Lab integration
- Radiology integration
- Medical devices integration
What are the benefits of Medical Devices Integration Software?
The top four reasons to consider implementing such software into the hospital’s work.
- Integrated workflow. By integrating medical devices the hospital receives an efficient, easy, and understandable workflow. All the sections of the hospital are connected, and due to the web-based system, they can be easily controlled.
- Eliminating the manual work with health records and clinical data. Now the software for integration is able to collect and analyze the data automatically. The medical personnel will receive clear and processed information, probably even collected and summed up from more than one device at a time. So the process goes way faster increasing data quality and eliminating all the possible errors due to human factors.
- Remote control. Now doctors can watch over the health status of each patient even if they aren’t physically at the hospital. It can be possible due to the cloud-based online access to the information and the personal cabinet.
- Web-based storage. The received data from all the medical devices now will be filtered, stored, and secured online. This means that there is no more struggling with searching for the required patient’s data through all the devices and the system will collect everything automatically and send the data directly to the place of storage.
Read more about the integration of Healthcare IT:
Recent Posts
Archives
- December 2024
- November 2024
- October 2024
- September 2024
- August 2024
- April 2024
- February 2024
- January 2024
- April 2022
- November 2021
- August 2021
- May 2021
- April 2021
- March 2021
- February 2021
- December 2020
- November 2020
- October 2020
- July 2020
- April 2020
- December 2019
- October 2019
- August 2019
- July 2019
- June 2019
- April 2019